The ventral tegmentum is composed of anumber of neuronsthat are located in themidbrain. They are found on the floor of the brain close to the midline brain. The ventral tegmentum plays a significant role in a number of functions, including those associated withreward.
With the ventral tegmentum being involved in a large number of functions and therefore being of significant importance, this may seem rather intimidating. There is no need to be, and we will provide you with all you need to know about the ventral tegmentum, from where it is located, to what it does, as well as what will happen should this area become damaged or diseased.
.What Is The Ventral Tegmentum?Where is the Ventral Tegmentum Found?Parts of Ventral TegmentumWhat Hormone Does The Ventral Tegmentum Produce?What Is The Function Of The Ventral Tegmentum?Disorders And Disease Of The Ventral TegmentumConclusion
.
What Is The Ventral Tegmentum?
Where is the Ventral Tegmentum Found?
Parts of Ventral Tegmentum
What Hormone Does The Ventral Tegmentum Produce?
What Is The Function Of The Ventral Tegmentum?
Disorders And Disease Of The Ventral Tegmentum
Conclusion

The neurons of the ventral tegmentum help to form one of thetwo main dopaminergic centers in the brain, the other beingSubstantia Nigra. It is a tiny area of neurons that has many neural branches or axons that project out into the entire brain. These fibrous branches help to transmit various messages throughout the brain that help with bothemotional and cognitive functioning.
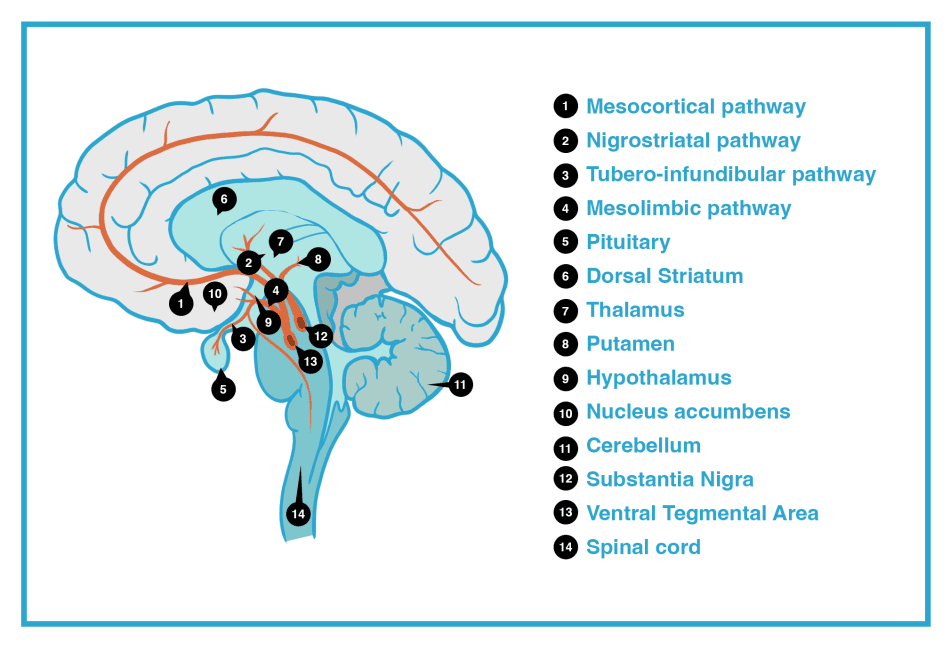
The ventral tegmentum is found at the base of the brain,just above the brain stem. Itneighbors the substantia nigra, which is the other major dopaminergic center of the brain laterally. There can often be very little physical difference between the ventral tegmentum and the substantia nigra, with both areas being very anatomically similar.
There are, however, differences in the neural pathways that lead off from both centers. There are many nerve pathways or efferent nerves that project from the ventral tegmentum,but the two main ones are the mesolimbic and the mesocortical pathways.
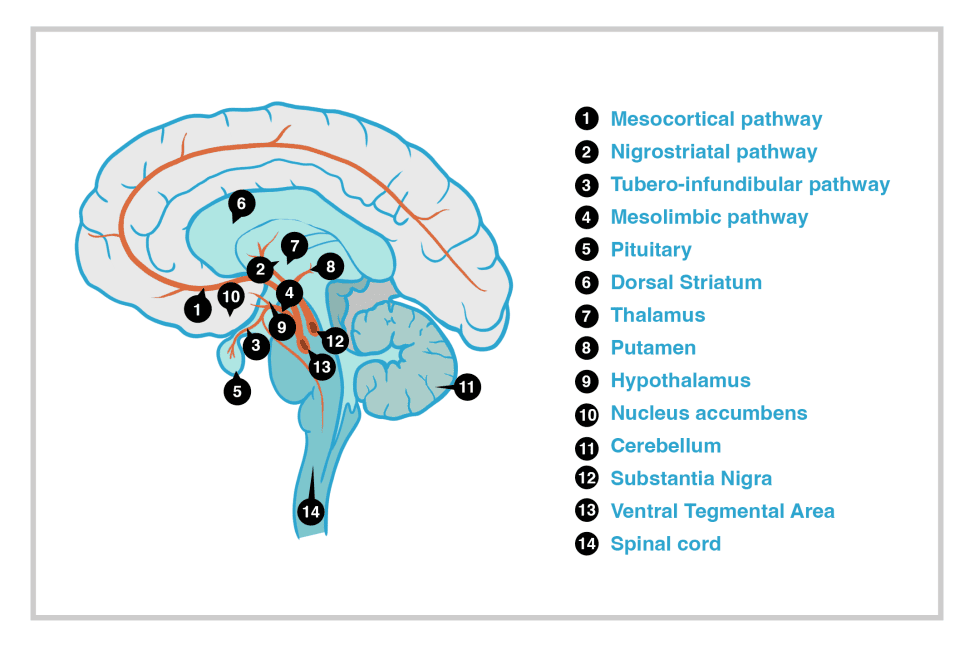
The ventral tegmentum is additionally found closer to the base of the brain, positioned almost centrally over the hippocampus region
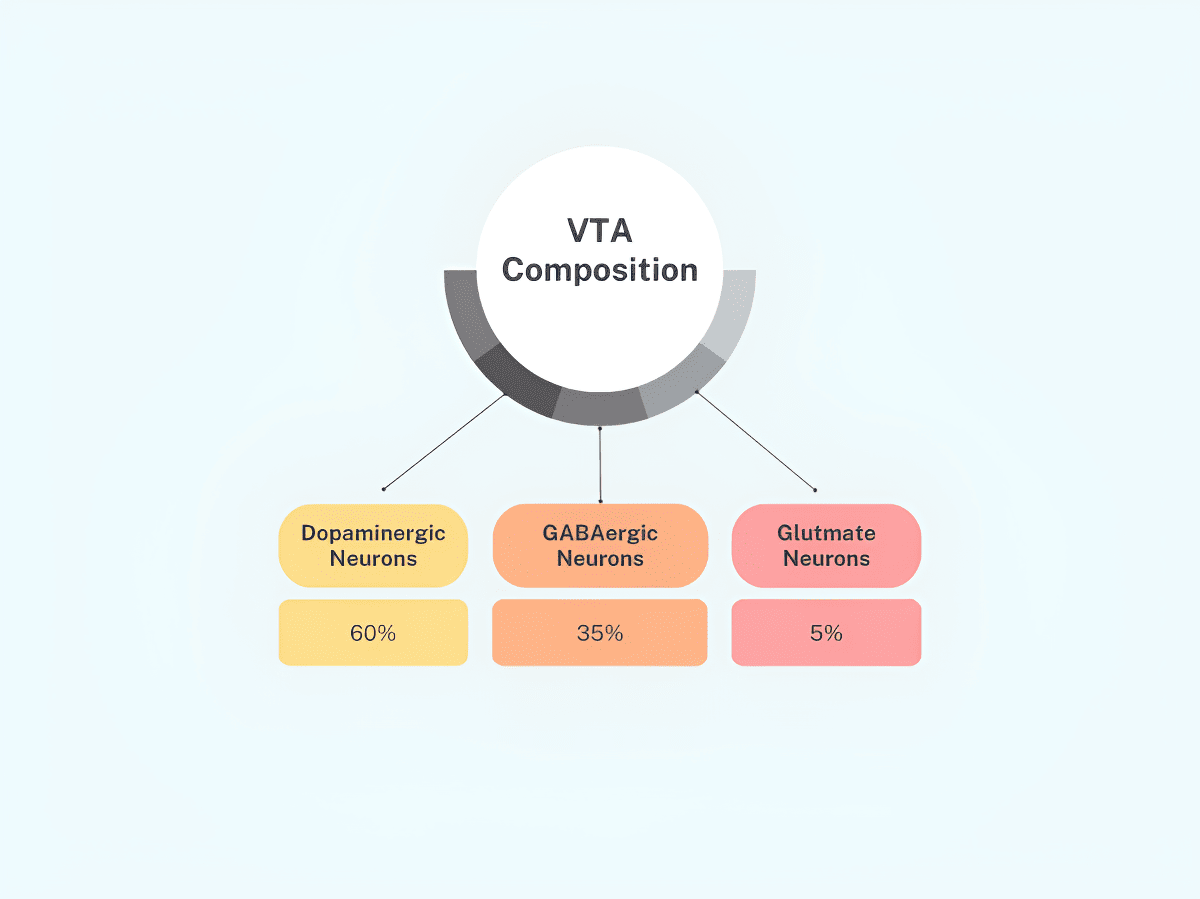
Of these four areas, thefirst twomentioned are largelydopaminergicneurons, while thelast mentionedis mainlyGABAergiccells.
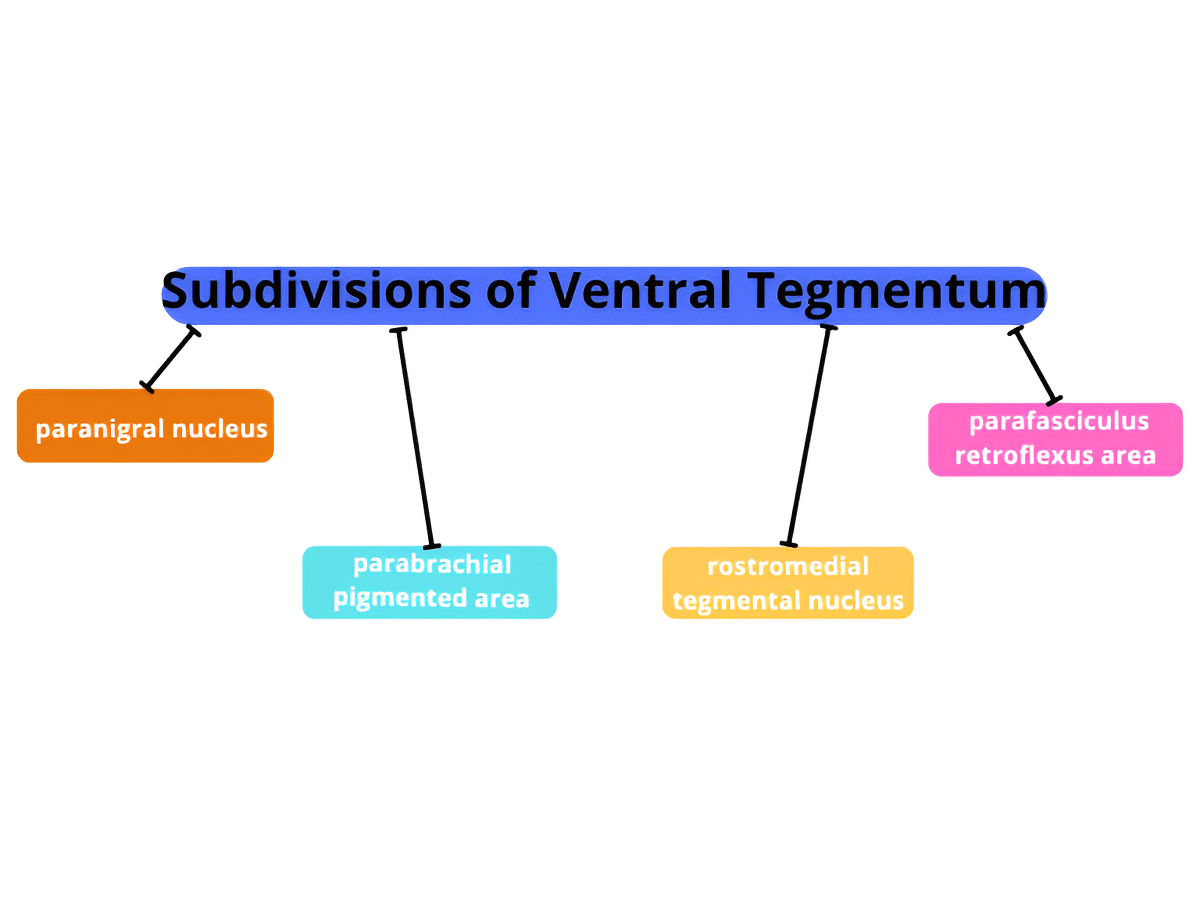
To orient ourselves with different parts lets look at a beautiful diagram
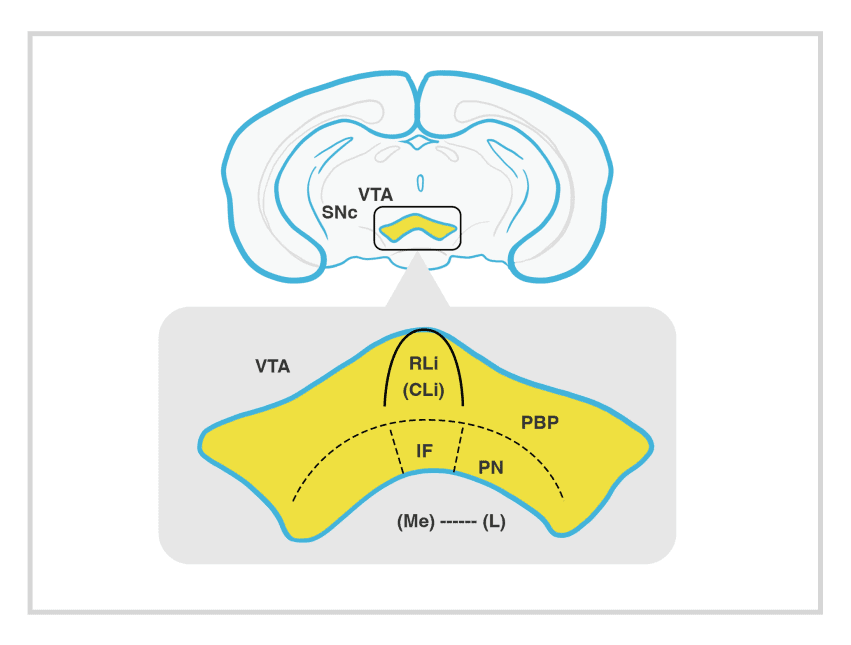
VTA= Ventral Tegmental Area, SNc= Substantia Nigra, PBP=Parabranchial Pigmented area, PN=Paranigral Nucleus, IF=Interfascial Nucleus or Para Fasiculus Reteroflux area , RLi= Roster Linear Nucleus or Rostro Medial Tegmental Nucleus
The projecting axons of the ventral tegmentum form themesocorticolimbicprojection, which is an important part of the limbic system.
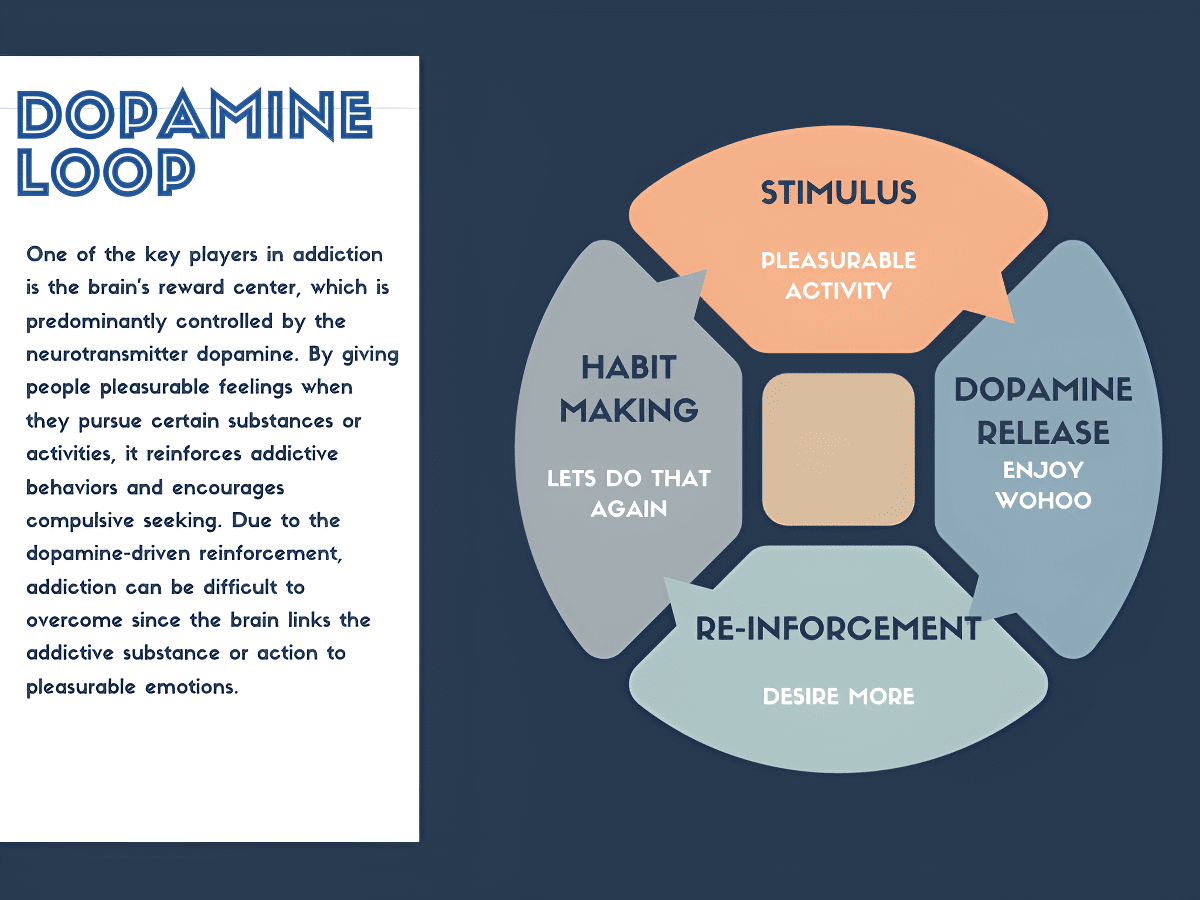
As noted above, the ventral tegmentum is one of the two main dopaminergic areas of the brain. It producesdopamine.We have a look at what dopamine is and what it does, as it is key to understanding the functions of the ventral tegmentum.
What Is Dopamine And What Is Its Function
Dopamine is a type of neurotransmitter molecule that functions as a neurotransmitter. Dopamine has long been considered the‘happy hormone’ due to its association with pleasure and habit formation. As mentioned, the cell bodies of the group of neurons that make up the ventral tegmentum are one of the areas that produce dopamine.
The ventral tegmentum has a great many functions but is most well-known for the several roles it performs in the cognitive and emotional functioning of the human brain.
When dopamine is released, it travels viatwo pathwaysas far Ventral Tegmentum is concerned ; the mesocortical pathway and the mesolimbic pathway. The two pathways are also known as the mesocorticolimbic projection when referred to together.
The mesocortical pathway leads to the prefrontal cortex, while the mesolimbic pathway leads to the nucleus accumbens.
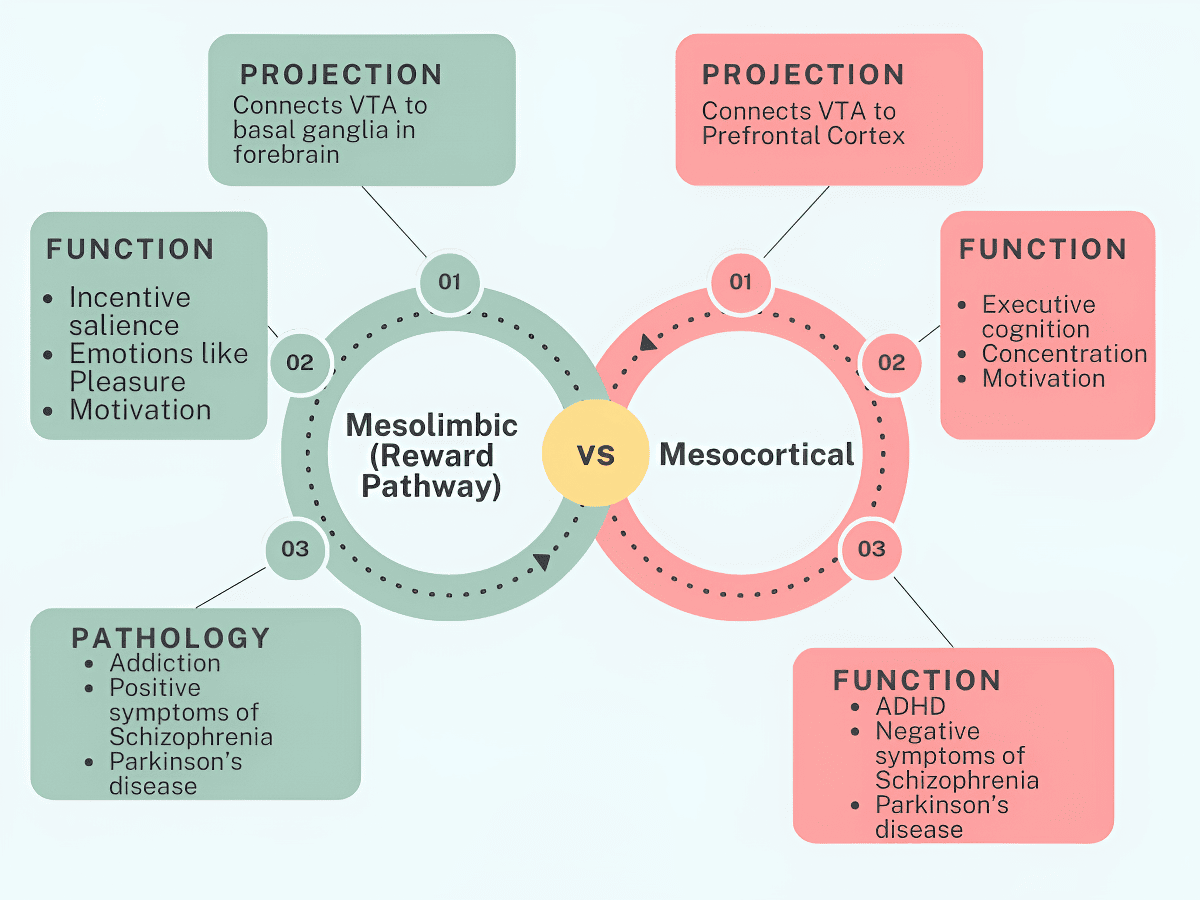
These pathways provide both input and output capability, and messages can be sent to the ventral tegmentum via these axons as well as to other parts of the brain from the ventral tegmentum.
The Most Well-known Function Of The Ventral Tegmentum
The most well-known function of the ventral tegmentum is the production and release of dopamine which has a critical role in functions such as:
These functions are all interrelated. The ventral tegmentum plays an integral part inhow the reward centerof the brain works.
When the body receives a reward-related stimulus, the ventral tegmentum releases dopamine which is sent via the nerves that project from the ventral tegmentum area. The dopamine will then travel along thismesolimbicpathway to the area in theforebrain, otherwise known as thenucleus accumbens.
In the nucleus accumbens, the dopamine message will help us to consider the rewards of the stimuli and as well as motivate us to achieve them. The ventral tegmentum is therefore responsible for theincentive saliencewe experience.
This happy, blissful feeling we experience then motivates us to want more of the stimulus that caused it.
This is why the ventral tegmentum can also be an integral factor in addiction. Drugs can overstimulate the production of dopamine, creating a craving for the stimulus that is never satisfied. This results inaddictive behaviorin the pursuit of the ‘happy’ or ‘high’ that is experienced under the influence of the drugs.
Through its dopamine production, the ventral tegmentum is also involved in reward cognition which is necessary for species survival. The brain is able to determine theimportance of something that is a good stimulus, and the dopamine release motivates the brain to want more of it.
Exercise, food, gifts, sex, praise, and admiration all serve as rewarding stimuli,and because of the good feeling we get from doing them, we are motivated to keep doing them. Thus resulting in better health, energy and ultimately survival.
Areas Linked To The Ventral Tegmentum Via Projections
Other than the prefrontal cortex and the nucleus accumbens, there are other areas of the brain that receive dopamine as a neurotransmitter via neural projections. These areas are:
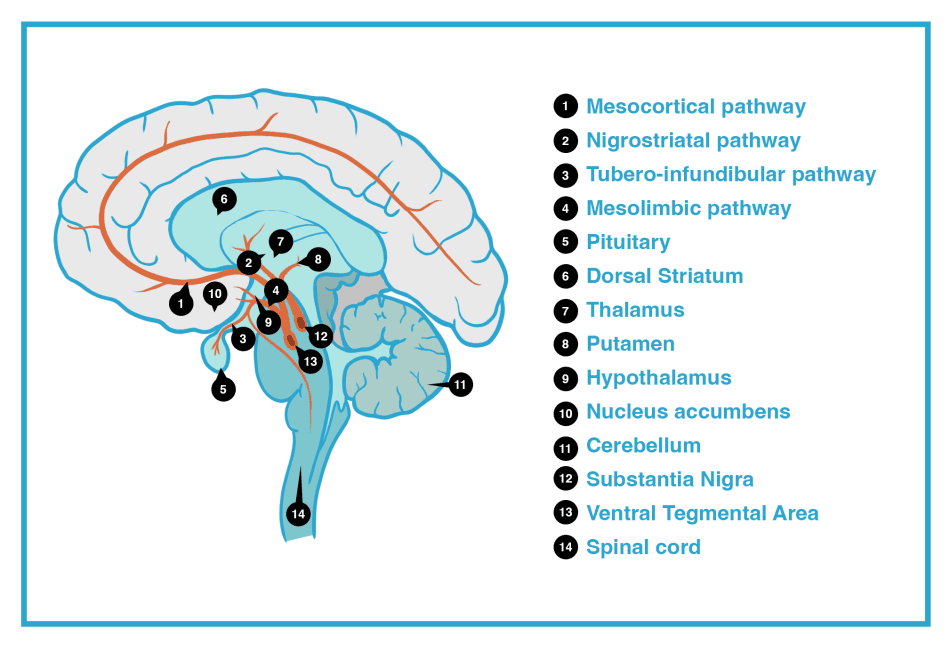
The widespread link of the ventral tegmentum to numerous parts of the brain helps explain how important it is in terms of properly functioning.
Theamygdalais responsible for memory and decision-making and will also play a role in reward and emotional responses. Theentorhinal cortexis also linked to memory. Theolfactory bulbis linked to the sense of smell and can have a bearing on the cognitive interpretation of smell.
Thecingulate gyrushas a bearing on motivation through behavior. TheHippocampusis associated with memory.
The majority of these brain areas form part of thelimbic loop or limbic system, and many have crucial roles in the development, formation and retention of memory. This commonality helps us to understand an injury or disease to the ventral tegmentum can impact numerous areas of the brain.
As the ventral tegmentum is a critical component of both the mesolimbic and the mesocortical pathways, any disruption to these pathways can result in several disorders and diseases.
Disorders Associated With The Ventral Tegmentum
There are a few disorders that are associated with a damaged ventral tegmentum.
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that exhibits the inability to think, feel, or behave in a connected manner. People who suffer from schizophrenia cannot perceive reality coherently and will often create illusions and fantasies that will seem real to them while they withdraw from real-world interactions.
Schizophrenia has a lot to do with how the midbrain functions. Damage or developmental problems in the midbrain are often linked to schizophrenic diagnosis. The ventral tegmentum is a significant part of the midbrain, albeit small in size. Its pivotal role as a dopaminergic center means that any damage to the area can have a severe impact on schizophrenics as well as be possible evidence of the disorder.
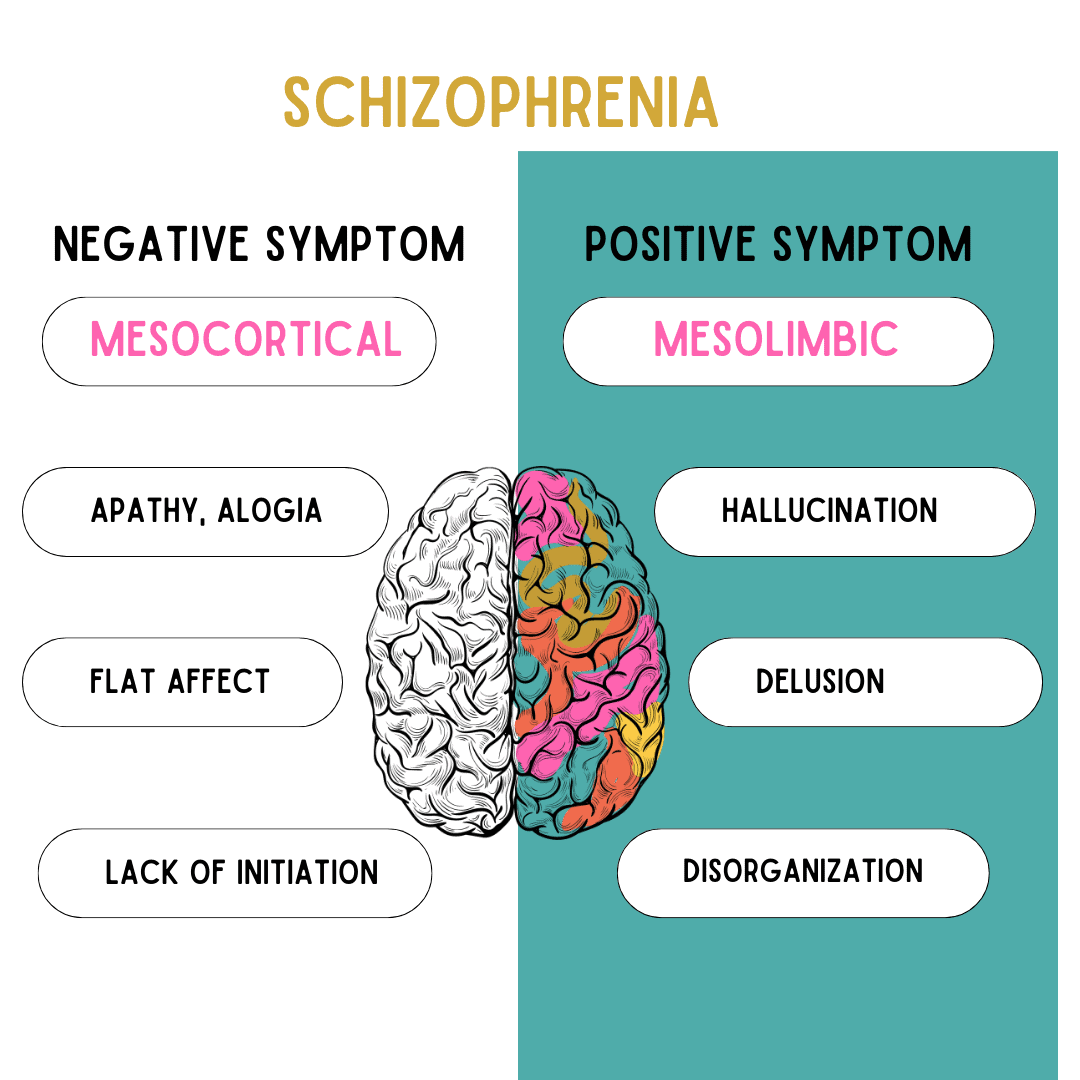
Schizophrenics have difficulty with memory and will additionally lack motivation. This memory loss can result in problems with decision-making – all of which are linked to the neurotransmitter dopamine.
This disorder is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is known as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). ADHD is more generally diagnosed in children but can also remain into adulthood. This disorder is displayed as behaviors likehyperactivity, difficulty concentrating on a single task for longer periods, general inattention, as well as impulsiveness.
ADHD has links to a number of areas of the brain. As more research is done, we learn more about the disorder and which areas of the brain may impact its manifestation and development. It should be noted that there are generally several factors involved in the behavioral traits of ADHD.
The location of the ventral tegmentum at the base of the brain above the brain stem is thought to have a part to play in the onset of ADHD when there are developmental delays. Thelimbic linkto several memory centers as well as the production of the hormone that governs pleasure response and incentive salience.
However, suppose there is delayed development in this area. In that case, the limbic system may not be able to function as well as stunts the ability of other areas that are responsible for memory, cognition or decision-making to misfire.
Disease Associated With The Ventral Tegmentum
The most common disease associated with damage or a breakdown of the functioning of the ventral tegmentum isParkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s is a condition in which brain areas become increasingly damaged over time. It is most common in the elderly, starting from about 60 years old but can develop as early as 50. Parkinson’s results in aninability to control one’s movements with early symptoms, including uncontrolled tremors of the limbs.
Ongoing and progressive damage of the ventral tegmentum and other areas of the midbrain, like the substantia nigra will result in reduced dopamine production. Damage will occur in the limbic pathways, meaning that whatever dopamine is produced will have difficulty getting to where it needs to be to assist in proper bodily functions.
The ventral tegmentum, although significantly smaller than many areas of the brain, plays an integral role in brain functions. It plays a pivotal part in the limbic system, with its neural axons formingmesocorticolimbicprojections that are the pathways for dopamine, amongst other hormones. This area is essential in how thebrain translates reward stimuli, motivation, and pleasure.
The ventral tegmentum’s close association with several crucial brain areas through the limbic pathway system makes its damage or disease a serious complication that can result in numerous disorders and diseases such as schizophrenia, ADHD, as well as Parkinson’s disease.
Related posts:Ventral Root (Location + Function)Ventral Stream (Location + Function)Nucleus AccumbensThe Mesocortical Pathway (Location, Function, and Images)The Psychology of Long Distance Relationships
Related posts:
Reference this article:Practical Psychology. (2022, September).Ventral Tegmentum.Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/ventral-tegmentum/.Practical Psychology. (2022, September). Ventral Tegmentum. Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/ventral-tegmentum/.Copy
Reference this article:
Practical Psychology. (2022, September).Ventral Tegmentum.Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/ventral-tegmentum/.Practical Psychology. (2022, September). Ventral Tegmentum. Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/ventral-tegmentum/.Copy
Copy