In Chuck Palahniuk’s Invisible Monsters, he writes, “Nothing of me is original. I am the combined effort of everyone I’ve ever known.” This sentiment will sound familiar as you learn about Lewin’s Field Theory.
What Is Lewin’s Field Theory?About Kurt LewinField Theory Concepts and ExamplesKurt Lewin’s Other Contributions to Social PsychologyKurt Lewin Quotes From Field Theory in Social Science
What Is Lewin’s Field Theory?
About Kurt Lewin
Field Theory Concepts and Examples
Kurt Lewin’s Other Contributions to Social Psychology
Kurt Lewin Quotes From Field Theory in Social Science
Invisible Monsters was not about Kurt Lewin or psychological theories, but this quote certainly speaks to what we will discuss today. Although, if it were up to Lewin, this quote would be altered slightly.
Lewin’s Field Theory suggests that you are a combination of everything you’ve ever known. The theory posits that human behavior results from the interplay between the individual and their environment.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
In essence, Lewin’s Field Theory offers a comprehensive lens to view behavior as a dynamic interplay between an individual and their environment, emphasizing the importance of context in shaping our actions.
There are many “field theories” out there. Lewin’s Field Theory exists within the world of physics. It has nothing to do with quantum field theory or crystal field theory. Einstein’s Unified Field Theory may be similar to Lewin’s Field Theory, suggesting that “everything” is connected. Still, most field theories exist within physics, not psychology.
If you are interested in learning about social psychology, read on!
 Kurt Lewin
Kurt Lewin
Kurt Lewin was a psychologist born in Poland in the late 1800s. He studied psychology in Germany and later emigrated to America. Working closely with Gestalt psychologists, he developed Field Theory and other ideas on change, education, and learning. Throughout his career, Lewin had a mission to use psychology to understand and overcome prejudice. His work set the foundations for “sensitivity training.” Lewin also mentored Leon Festinger, who went on to developCognitive Dissonance TheoryandSocial Comparison Theory.
Lewin was also known for his work connecting the worlds of psychology, mathematics, and topography. Field Theory is also known as “Topological and Vector Psychology.”
Influence Of Gestalt Theory
Lewin used concepts from Gestalt psychology to create Field Theory. Gestalt psychology was developed in the early 19th century and introduced new ideas about perception. At the time, structuralism was the dominant school in psychology. Structuralism attempted to break down the adult mind into each of its parts and analyze how these parts fit together.

Field
Lewin also took inspiration from mathematics and physics to “map out” an individual’s field. (The field is also known as the environment.) Within an individual’s environment are all factors that may influence a person’s decisions or behaviors.
Examples of these factors include:
These fields may be similar from person to person, but no two fields will look the same. Each environment is ultimately different, as it comprises all of an individual’s experiences and feelings, many of which are unique to them.
Life-Space
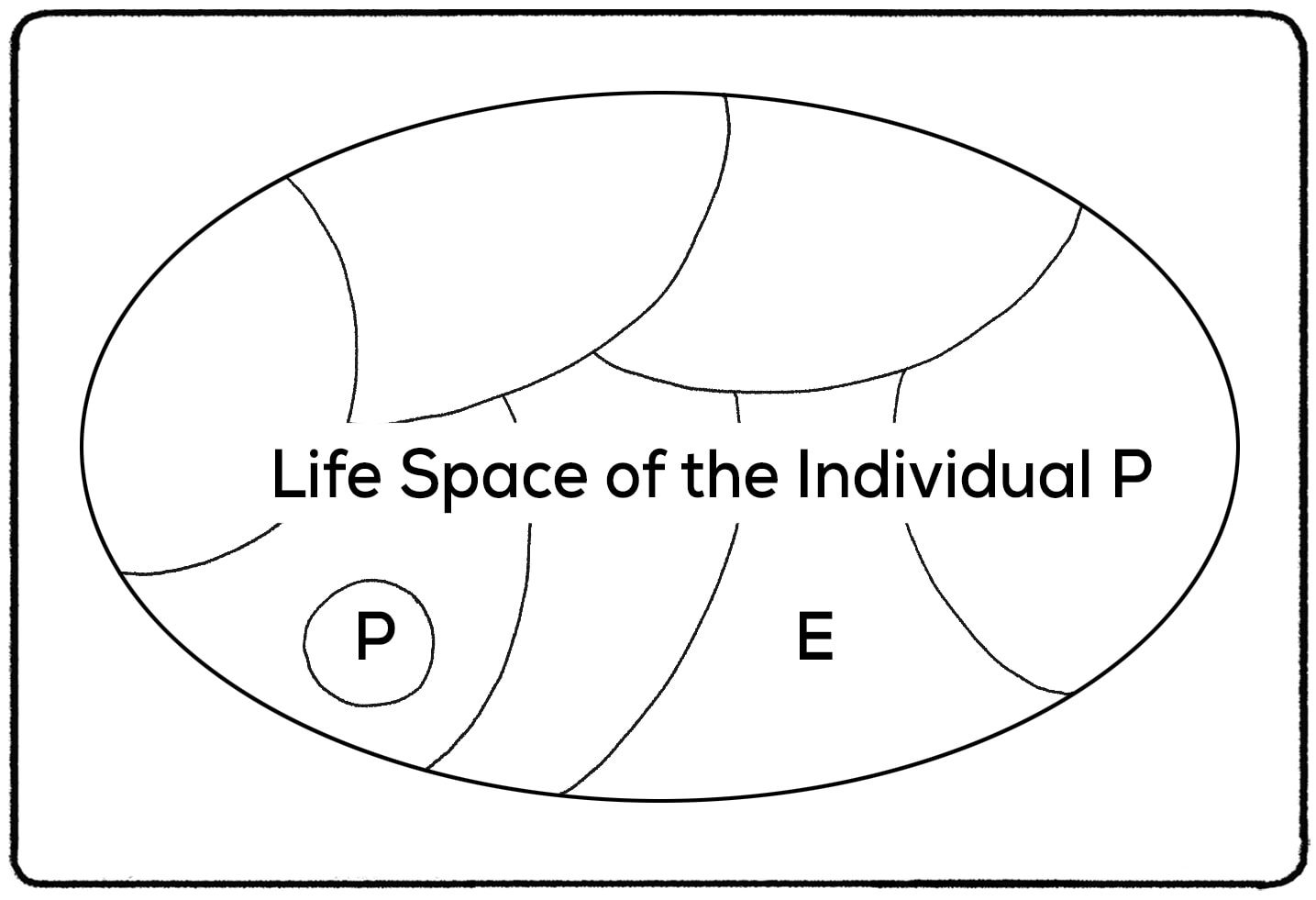
B = f (P, E)
Let’s break the equation down further. Lewin believed that the person and their environment ultimately determined the individual’s behavior, or B= f(LS) = F(P,E). I discussed the environment earlier in the video, but what exactly is the “person?”
Lewin used ideas from Gestalt Theory to define this term.
Examples of factors that make up the “person” include:
The life space is dynamic. Every day comes with new experiences. As individuals develop, learn, and change, their “person” will change and mold their life space.
The interaction between the person and what they’ve experienced will ultimately determine their behavior.
Here’s what Kurt Lewinhad to say about the life-spacein his bookField Theory as a Social Science:
“The life space… includes both the person and his psychological environment. The task of explaining behavior then becomes identical with (1) finding a scientific representation of the life space (LSp) and (2) determining the function (F) which links the behavior to the life space. This function (F) is what one usually calls a law… The novelist who tells the story behind the behavior and development of an individual gives us detailed data about his parents, his siblings, his character, his intelligence, his occupation, his friends, his status. He gives us these data in their specific interrelation, that is, as part of a total situation. Psychology has to fulfill the same task with scientific instead of poetic means….
The method should be analytical in that the different factors which influence behavior have to be specifically distinguished. In science, these data have also to be represented in their particular setting within the specific situation. A totality of coexisting facts which are conceived of as mutually interdependent is called a field. Psychology has to view the life space, including the person and his environment, as one field.“
Goals, Barriers, Conflicts
According to Lewin, an individual’s environment is not just a collection of experiences. Maps of a person’s environment may also include their goals and any barriers preventing them from reaching them. These goals may include things that the individual wants to achieve (positive valence) or goals that include things that the individual is trying to avoid (negative valence.)
As people overcome certain barriers or conflicts, their life-space will continue to mold and change.
Until Field Theory, psychologists focused more on an individual’s behavior and how it could be understood or altered. Lewin was one of the first psychologists to examine how individuals interacted with their environments and each other. For this reason, he is considered the “father” of social psychology.
Throughout his development of Field Theory and other ideas, Lewin brought ideas from mathematics and science into psychology. He was one of the first psychologists to pull ideas from the scientific method and apply them to social psychology. Rather than observing individuals and their interactions, he controlled elements of the environment and pioneered the way that psychologists conducted experiments.
Lewin’s contributions to the world of psychology are numerous. Without his work and the ideas within Field Theory, the world of social psychology would probably look drastically different.
Change Theory vs. Field Theory
Kurt Lewin’s Field Theory is arguably his most well-known contribution to social psychology, but he also developed Change Theory. Kurt Lewin’s Change Theory is quite different from field theory in that it tries to explain how we can reject and replace the information that we have learned. Lewin developed an unfreeze-change-refreeze model that instructs individuals and teams on changing their thinking and behavior. You can learn more about this theoryhere!
Kurt Lewin Quotes FromField Theory in Social Science
Interested in reading more about field theory? BorrowField Theory in Social Sciencefrom your local library. Here are some notable quotes from the book:
Related posts:Kurt Lewin Biography - Contributions To PsychologyLewin’s Change Theory (Definition + Examples)40+ Famous Psychologists (Images + Biographies)7 Gestalt Principles (Definition + Examples)Leon Festinger (Psychologist Biography)
Related posts:
Reference this article:Practical Psychology. (2020, April).Lewin’s Field Theory (Social Development).Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/lewins-field-theory/.Practical Psychology. (2020, April). Lewin’s Field Theory (Social Development). Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/lewins-field-theory/.Copy
Reference this article:
Practical Psychology. (2020, April).Lewin’s Field Theory (Social Development).Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/lewins-field-theory/.Practical Psychology. (2020, April). Lewin’s Field Theory (Social Development). Retrieved from https://practicalpie.com/lewins-field-theory/.Copy
Copy